The Root
• The primary root are designed by the direct
elongation of the radicle and develops inside the soil, in mainstream of the
dicotyledonous plants. The primary root has numerous orders of lateral roots and
these are termed as secondary, tertiary, etc. roots.
Different types of roots are:
·
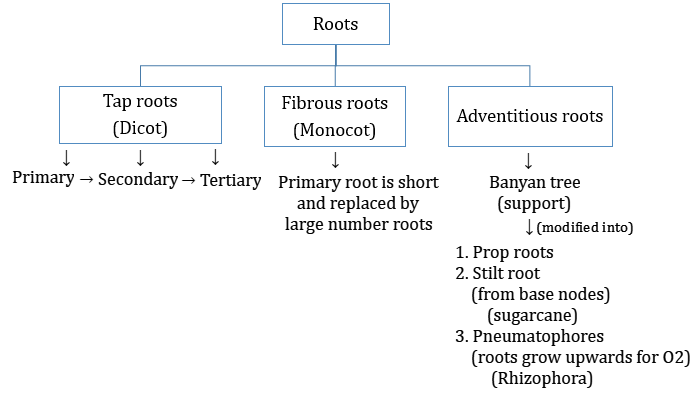
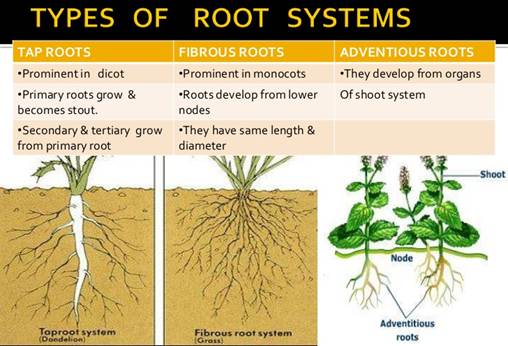
Tap roots
·
Fibrous roots
·
Adventitious roots
Tap
root:
The
primary root with its branches form the tap root system. Ex., Mustard plants.
Tap roots
Fibrous
Root:
The primary root are short lived in monocotyledonous
plants and it is replaced by a large number of roots, which originate from the
base of the stem and constitute the fibrous root system. Ex., Wheat plants.

Adventitious Root:
In some other plants like grass, Monstera
and the banyan tree, the roots are found arising from parts of the plants other
than the radicle and it is termed as adventitious roots.

• The role of roots are to absorb water and
minerals from the soil, providing a proper waterfront to the plant parts,
storage of reserve food materials and amalgamation of plant growth regulators.
Regions of the Root:
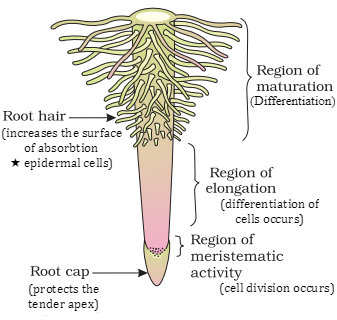
The regions of the root-tip
• The root is covered at the apex by a protector like
structure called root cap, which protects the tender apex of the root as it
penetrates through the soil. The area above the root cap is the region of
meristematic activity.
• The cells in this region divide constantly,
they are small, thin walled and with solid protoplasm. The cells adjacent to
this region experience speedy elongation and increase and are the prime cause
for the growth of root length. This specific region is called as region of
elongation.
• The cells in this zone slowly distinguish and
develop and this region is region of maturation.
• Some of the epidermal cells in this region form
very fine, delicate thread like assemblies called, root hairs, which absorbs
water and minerals from the soil.
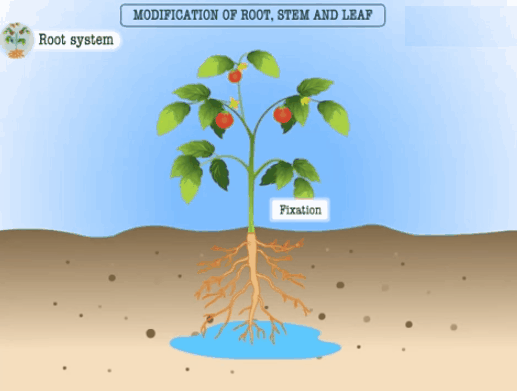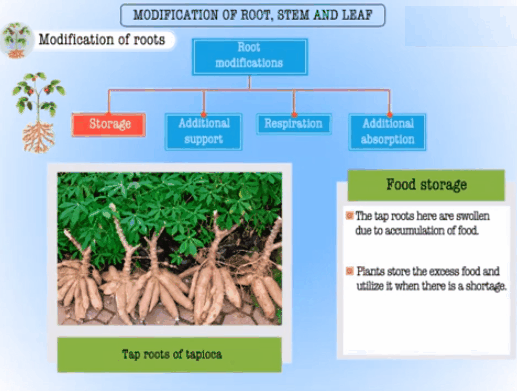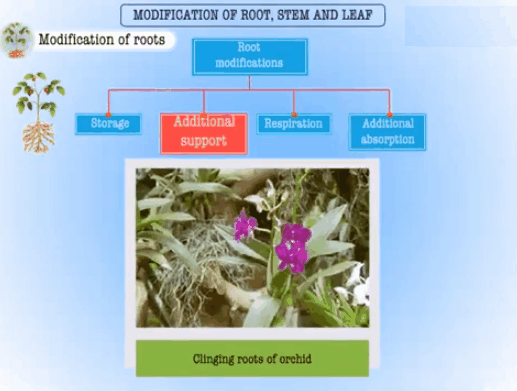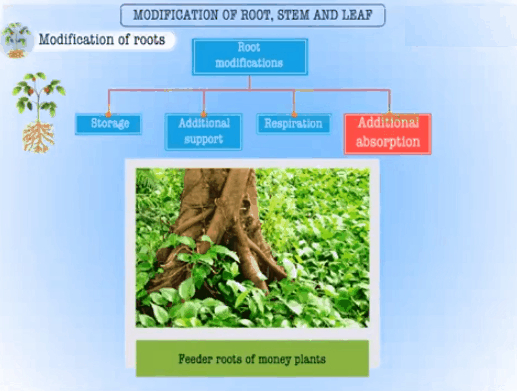
Modifications of Root:
• The roots of some plants changes their shape
and structures to suit themselves to perform functions like support, storage of
food and respiration. Ex., Tap roots of carrot, turnip and adventitious roots
of sweet potato, get enlarged and store food.
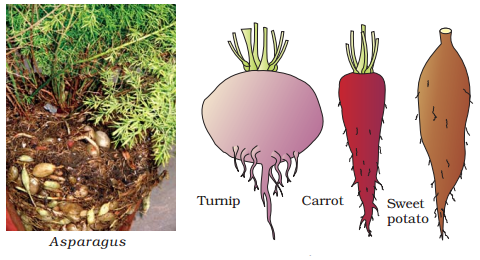
Modification
of root for storage
• Those hanging structures that support a banyan
tree are termed as prop roots. Supporting roots arising from the lower nodes of
the stem are stilt roots. Ex., stems of maize and sugarcane.
• In some plants growing in swampy areas, many
roots comes out of the ground and grows vertically up and these are
Pneumatophores assists to get oxygen for respiration. Ex., Rhizophora.

Modification
of root for respiration: pneumatophore in Rhizophora