The Stem
• The stem is the mounting portion of the axis with branches,
leaves, flowers and fruits. The stem grows from the plumule
of the embryo of a germinating seed.
• Nodes and internodes are the regions available in the stem.
Nodes are the area of the stem where the leaves are born and the internodes are
the portion between the two nodes.
• The stem do have buds which may be terminal or axillary.
The colours of the stem are greenish in the young periods and attains woody and
dark brown frequently in the later stages.
• The main functions of the stem are distribution of branches
bearing leaves, flowers and fruits.

It also conducts water, minerals from the soil,
photosynthesis and some make the role of food storage, support, protection and
vegetative propagation.
Modifications
of Stem:
|
Part |
Modification |
Example |
|
Underground stem |
Stem (to tide over unfavourable
condition) |
Zaminkand, colocasia |
|
Tendrils |
Stem (for climbing) |
Cucumber, pumkin, watermelon
and grape vines |
|
Thrones |
Axillary bud (Protection) |
Citrus, bogainvilla |
|
Fleshy stem |
(i) Flattened (ii) Cylindrical (have chlorophyl) |
(i) Opentia (ii) Euphorbia |
|
Underground stem |
Stem (vegetative propagation) |
Grass, strawberry |
|
Lateral branches |
Stem (vegetative
propagation) |
Mint and jasmin |
|
Lateral branch |
Rosette of leaves (aquatic modification) |
Euchornia, pistia |
• Stems are adapted to accomplish numerous roles. Stems in
the underground store food, (Ex., potato, ginger, turmeric, zaminkand,
Colocasia) and also act as organs of perennation to
overcome the hurdles which is unfavourable for growth.

Modifications of stem for
storage
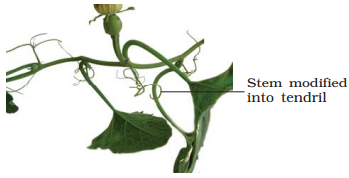
• Stem tendrils which grow from axillary buds are slender,
spirally coiled and help plants to climb as in case of gourds (cucumber,
watermelon, pumpkins) and grapevines.
Modifications of stem for
support

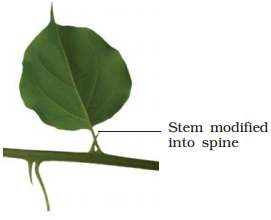
• Axillary buds of stems is also to get adapted in to woody,
straight and pointed thorns. The thorns defend plants from glancing animals.
Ex., Citrus, bougainvillea.
Modifications of stem for
protection
• Some plants of dry regions adapt their stems into a
flattened (Opuntia), or fleshy cylindrical
(Euphorbia) structures and they contain chlorophyll and carry out
photosynthesis.
• Certain underground stems plants like grass and strawberry,
etc., spread to new positions, when older parts die to form new plants.
• In plants like mint and jasmine a slender lateral branch
arises from the base of the main axis and after growing aerially for some time
arch towards the ground.

Modifications
of stem for spread and vegetative propagation
• A lateral branch with short internodes and each node
bearing a rosette of leaves and a tuft of roots is found in aquatic plants like
Pistia and Eichhornia.
• In banana, pineapple and Chrysanthemum, the lateral
branches originate from the basal and underground portion of the main stem,
grow horizontally beneath the soil and then come out indirectly upward giving
rise to leafy shoots.