The Leaf
• The leaf is a lateral, flattened structure
borne on the stem, develops at the node and bears a bud in its axil. The
branches develop from axillary bud later. Leaves originate from shoot apical
meristems and are set in an acropetal order and
leaves are the most important vegetative organs for photosynthesis.
A characteristic leaf has three main parts:
·
Leaf base
·
Petiole
·
Lamina
Parts of
a leaf
• The leaf is attached to the stem by the leaf
base and may bear two lateral small leaf like structures called stipules.
• In monocotyledons, the leaf base expands into a
sheath covering the stem partially or wholly. In some leguminous plants the
leaf base may become swollen, which is called the pulvinus.
• The petiole help hold the blade to light. Long
thin flexible petioles allow leaf blades to flutter in wind, thereby cooling
the leaf and bringing fresh air to leaf surface.
• The lamina or the leaf blade is the green
expanded part of the leaf with veins and veinlets. There is, a middle prominent
vein, known as the midrib. Veins provide rigidity to the leaf blade and act as
channels of transport for water, minerals and food materials.
• The shape, margin, apex, surface and extent of
incision of lamina varies in different leaves.
Venation:
• The organization of veins and the veinlets in
the leaf lamina is termed as venation. When the veinlets form a system, the
venation is termed as reticulate.

Reticulate
venation
• When the veins run parallel to each other
within a lamina, the venation is termed as parallel.

Parallel
venation
• Leaves of dicotyledonous plants typically have
reticulate venation, while parallel venation is the characteristic of most
monocotyledons.
Types of Leaves:
• A leaf is said to be simple, if its lamina is
full or when incised, the incisions do not touch the midrib. When the incisions
of the lamina stretch to the midrib breaking it into a number of leaflets, then
it is compound.
• A bud is existing in the axil of petiole of
both simple and compound leaves, but not in existence in the axil of leaflets
of the compound leaf.
The compound leaves is of two types:
·
Pinnately compound leaf
·
Palmately compound leaves
• Pinnately compound leaf has a number of
leaflets on a common axis, the rachis, which represents the midrib of the leaf.
Ex., neem.

Pinnately
compound leaf
• Palmately compound
leaves, has the leaflets attached at a common point, i.e., at the tip of
petiole. Ex., silk cotton.

Palmately compound leaf
Phyllotaxy:
Phyllotaxy is the pattern of organization of leaves on the stem or
branch and is of three types –
·
Alternate
·
Opposite
·
Whorled
• In alternate type of phyllotaxy,
a single leaf arises at each node in alternate manner. Ex., China rose, and
mustard, sun flower plants.
• In opposite type, a pair of leaves arise at
each node and lie opposite to each other. Ex., Calotropis
and guava plants.
• If more than two leaves arise at a node and
form a whorl, it is termed as whorled. Ex., Alstonia.
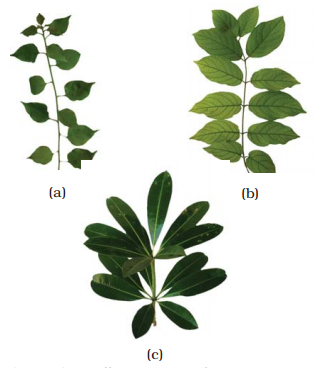
Different
types of phyllotaxy : (a) Alternate (b) Opposite (c) Whorled
Modification of Leaves:
·
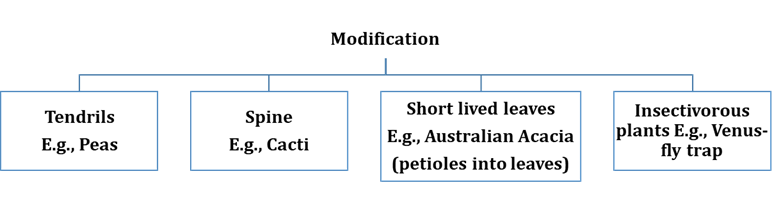
Leaves are quite frequently
modified to do roles other than photosynthesis.
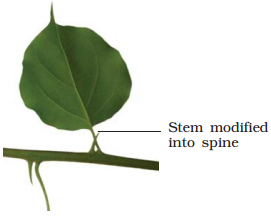
·
They are converted into
tendrils for climbing ex., peas or into spines for defence ex., cacti.
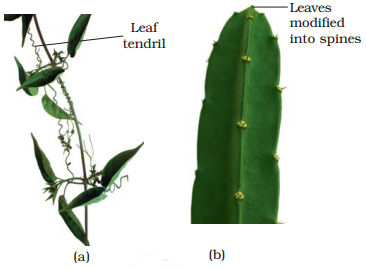
Modifications
of leaf for : (a) support: tendril (b) protection:
spines
·
The fleshy leaves of onion
and garlic store food.

Modifications
of leaf for : storage: fleshy leaves
·
The leaves are small and
short-lived, in plants such as Australian acacia.
·
In these plants, the
petioles expand, become green and synthesise food.
·
Certain insectivorous
plants leaves like pitcher plant, venus-fly trap are
also modified leaves.

Modification of leaf