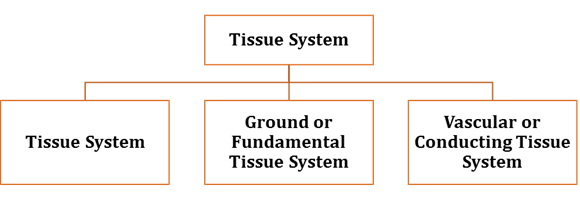
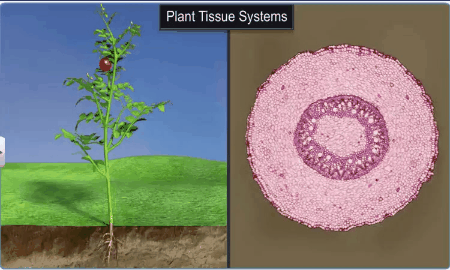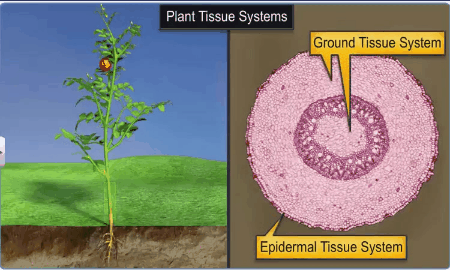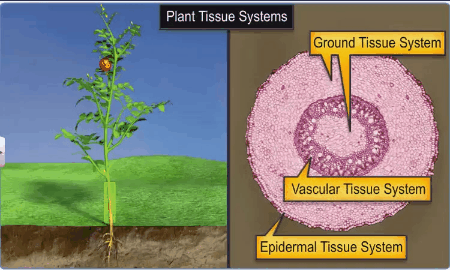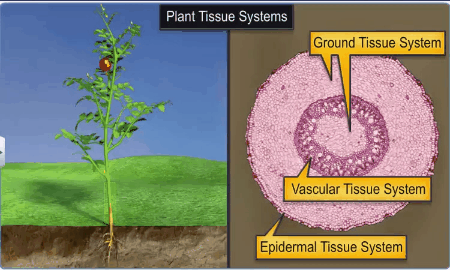
The Tissue System
The
structure of tissues and their functions is dependent on location.
On the
basis of their structure and location, there are three types of tissue systems.
These are
ท
The Epidermal Tissue System
ท
The Ground or Fundamental Tissue System
ท
The Vascular or Conducting Tissue System
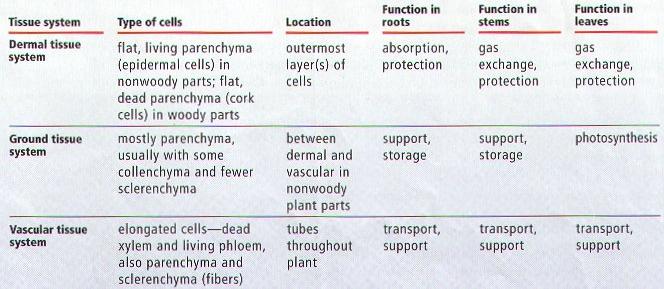
Epidermal Tissue System:
The
epidermal tissue system forms the outer covering of the entire plant body and
contains epidermal cells, stomata and the epidermal appendages the trichomes and hairs.
The epidermis
is the outermost layer of the primary plant body, made up of elongated,
compactly arranged cells, which form a continuous layer and is usually single
layered.
Epidermal cells are parenchymatous with an
insignificant amount of cytoplasm lining the cell wall and a large vacuole. The
outer epidermis is with a waxy thick layer called the cuticle which prevents
the loss of water and is absent in roots.
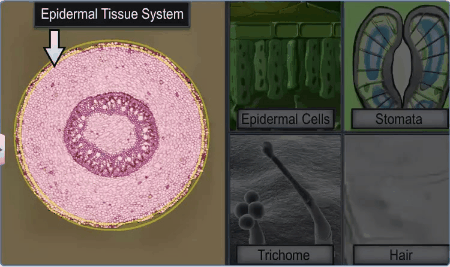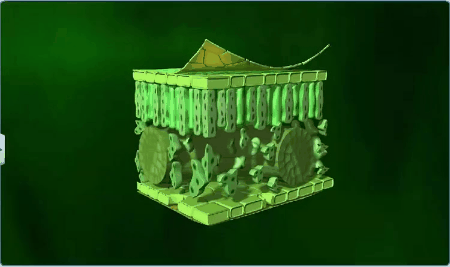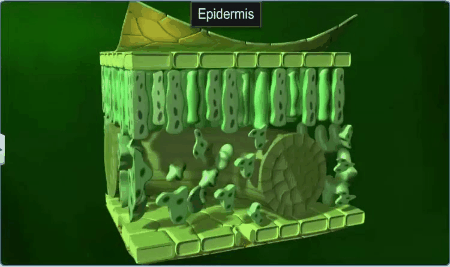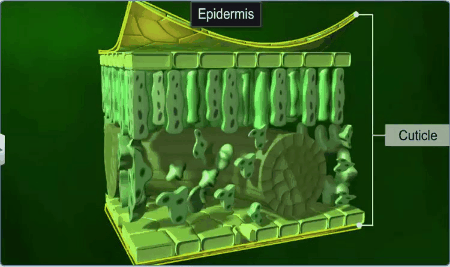
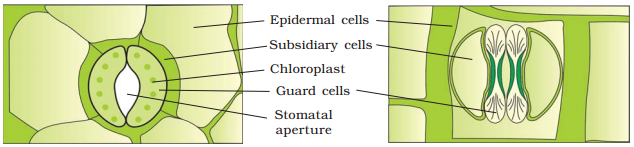
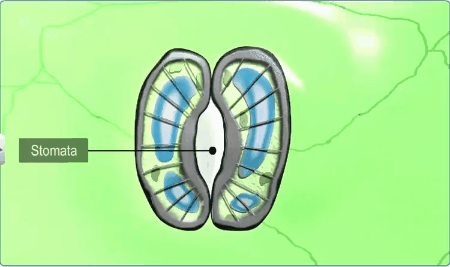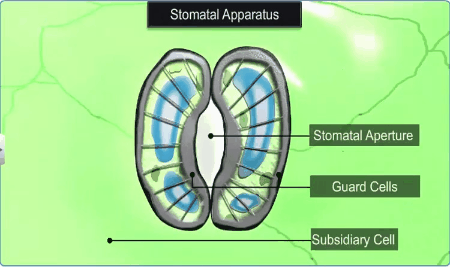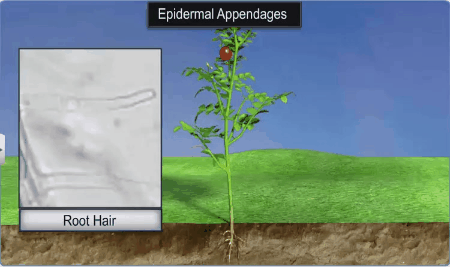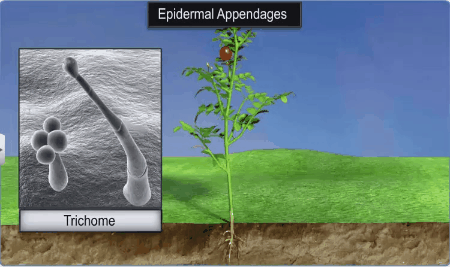
Stomata
are structures present in the epidermis of leaves, regulate the process of
transpiration and gaseous exchange. Each stoma is composed of two bean shaped
cells known as guard cells which enclose stomatal pore. In grasses, the guard
cells are dumb-bell shaped.
The
outer walls of guard cells (away from the stomatal pore) are thin and the inner
walls (towards the stomatal pore) are very thick and these guard cells possess
chloroplasts which regulate the opening and closing of stomata.

Sometimes, a few epidermal cells, in the vicinity of the guard cells become specialised
in their shape and size and are known as subsidiary cells.
The
stomatal aperture, guard cells and the surrounding subsidiary cells are
together called stomatal apparatus.
Diagrammatic representation: (a) stomata with bean-shaped guard cells
(b) stomata with dumb-bell shaped guard cell
The cells of epidermis bear a number of hairs. The root
hairs are unicellular elongations of the epidermal cells, helps to absorb water
and minerals from the soil.
On the stem the epidermal hairs are called trichomes. The trichomes in the
shoot system are usually multicellular. They may be branched or unbranched and
soft or stiff and even may be secretory. The trichomes
assists in preventing water loss due to transpiration.
The Ground Tissue System:
All tissues except epidermis and vascular bundles
constitute the ground tissue.
It consists of simple tissues such as parenchyma,
collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
Parenchymatous cells are usually
present in cortex, pericycle, pith and medullary
rays, in the primary stems and roots.
In leaves, the ground tissue consists of thin-walled
chloroplast containing cells and is called mesophyll.
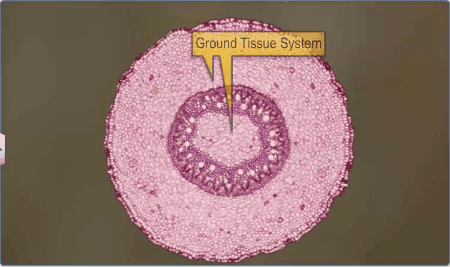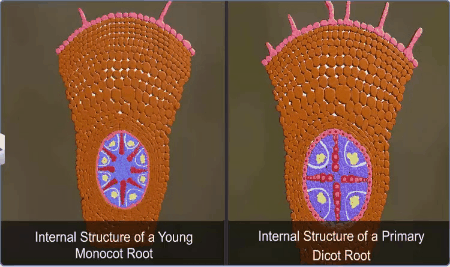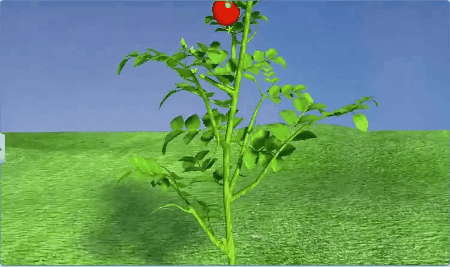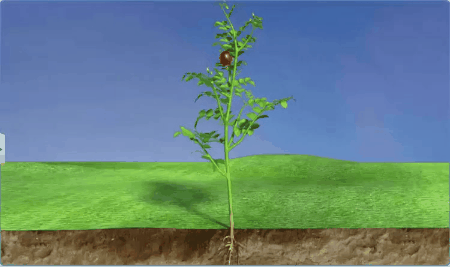
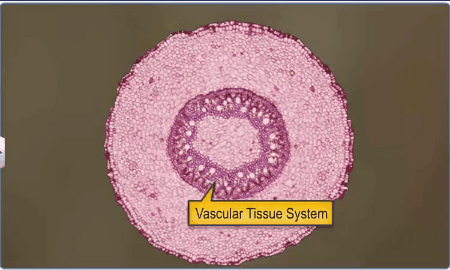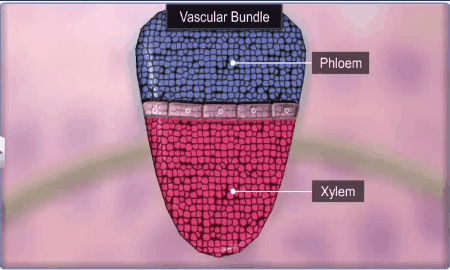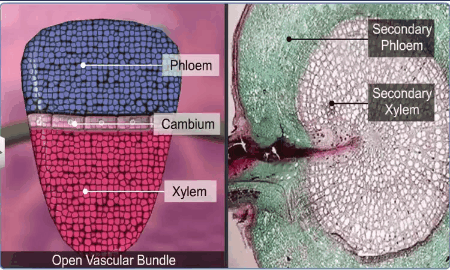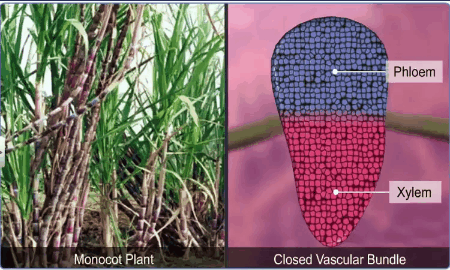
The Vascular Tissue System:
The vascular system consists of complex tissues, the phloem
and the xylem.
Both the xylem and phloem constitute vascular bundles.
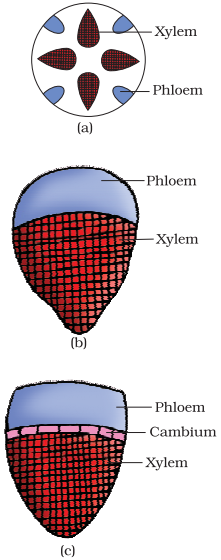
Various types of vascular bundles: (a) radial (b) conjoint closed
(c) conjoint open
In dicotyledonous stems, cambium is present between phloem
and xylem. Such vascular bundles because of the presence of cambium have the
potential to form secondary xylem and phloem tissues, and called as open
vascular bundles.
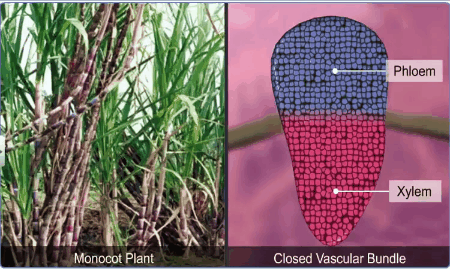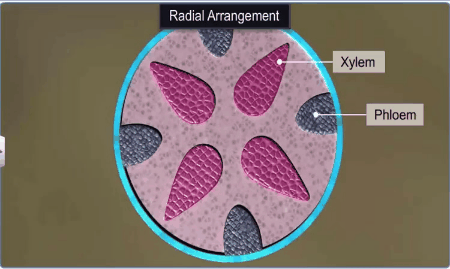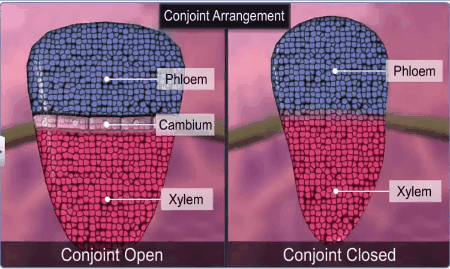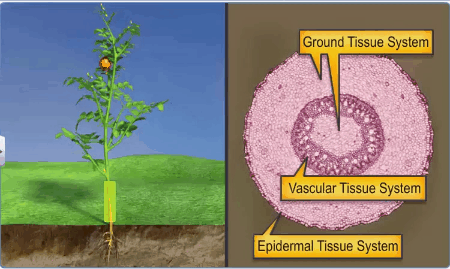
In the monocotyledons, the vascular bundles have no cambium
presence, since they do not form secondary tissues and are referred to as
closed.
When xylem and phloem within a vascular bundle are arranged
in an alternate manner on different radii, the arrangement is called radial
such as in roots.
In conjoint type of vascular bundles, the xylem and phloem
are situated at the same radius of vascular bundles. Such vascular bundles are
common in stems and leaves. The conjoint vascular bundles usually have the
phloem located only on the outer side of xylem.